Environment
Environmental Management
JLL Group Environmental Conservation Policy
We, JLL Group, think the promotion of sustainability is very important. We are committed to fulfilling our responsibilities as a member of society through the following initiatives to preserve the global environment.
1. Reduce the risk of environmental pollution
- We are committed to providing environmentally friendly products throughout the entire process of design, development, production, sales, use, and disposal of medical devices.
- In all of our business activities, we will not use prohibited hazardous chemicals and will manage the chemical substances contained in our products.
2. Promote environmental preservation
- To cope with climate change, we will work to reduce greenhouse gas emissions through the use of renewable energy and the promotion of energy conservation.
- To create a recycling-oriented society, we will work toward zero emissions by efficiently using and reusing limited resources.
- To coexist in harmony with nature, we will engage in responsible procurement that takes into account the conservation and sustainability of water resources and biodiversity.
3. Comply with laws, regulations, ordinances, and other social norms
- We will comply with domestic and international environmental laws, regulations, ordinances, and agreements we have agreed to in all of our business activities.
4. Promote environmental management
- We will fulfill our accountability by proactively disclosing information on our environmental initiatives.
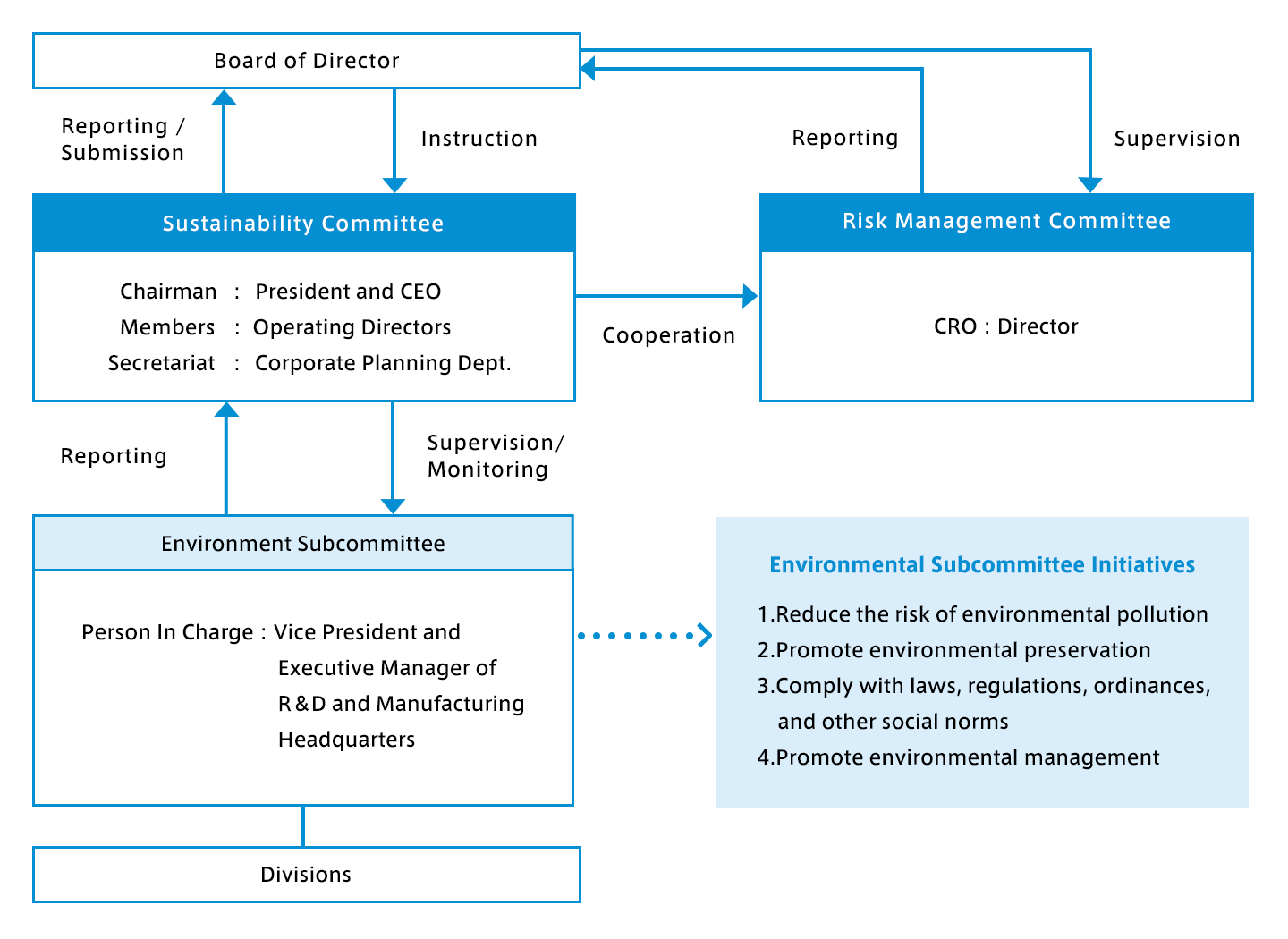
Environmental Promotion System
Under the direction of the Sustainability Committee, the Environment Subcommittee plays a central role in considering specific measures and promoting activities for environmental conservation. The Environment Subcommittee reports quarterly to the Sustainability Committee on the progress of activities, risk assessments, and countermeasures, and receives instructions as appropriate. In addition, with regard to climate change risks, the Sustainability Committee works together with the Risk Management Committee to share information and take other actions.
Realization of Environmental-Friendly Factories
We have three factories in Japan: Toda Factory (Saitama), Oyama Factory (Tochigi), and Ichihara Factory (Chiba). Each factory complies with the environmental laws and regulations of the region in which they are located and engages in production activities. There have never been any serious environmental accidents or leaks occurred in the factories.
Also, none of the three factories is located in areas that have a risk of damaging biodiversity.
Toda Factory and Medical Technology Park, where R&D functions are concentrated, are actively adopting energy-saving and environmental-friendly equipment such as LED lighting, double glazing, and rainwater utilization. As a result of these efforts, we have been rated as an “A” rank (BEE=2.1) by CASBEE*. Oyama Factory also uses the same equipment specifications as above.
In addition, Oyama Factory uses LED lighting and natural light. We have already switched to LED lighting at Ichihara Factory as well.
*Comprehensive Assessment System for Built Environment Efficiency
A method for evaluating and rating the environmental performance of buildings. The system comprehensively evaluates the quality of buildings. The list of evaluation items covers not only environmental factors such as energy efficiency and the use of materials and equipment with low environmental impact, but also indoor comfort and consideration for the landscape.

Medical Technology Park(North Square)
Disclosure based on TCFD Recommendations
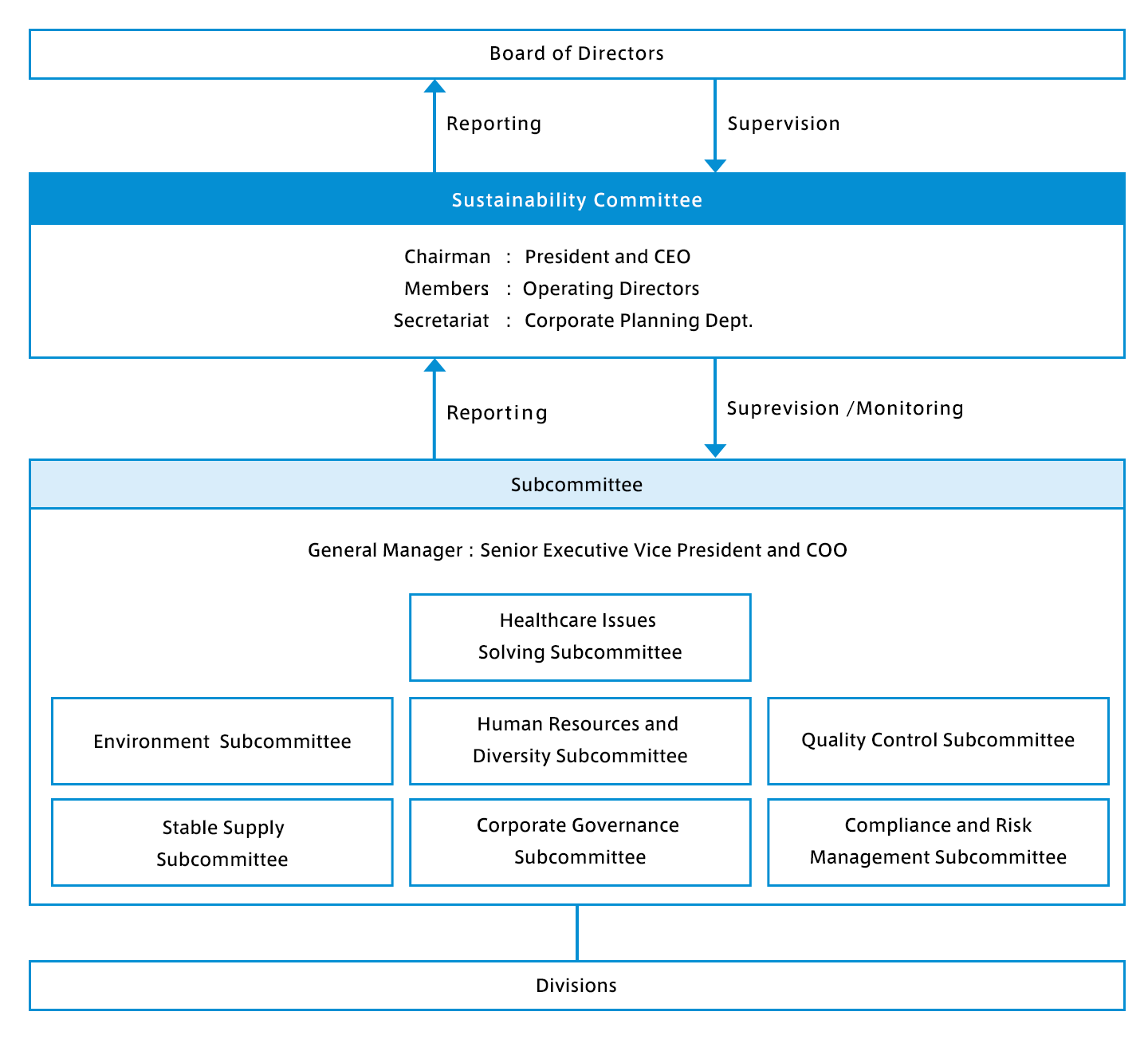
We consider the reduction of our environmental impact as one of our key issues, and we recognize that climate change is one of the most important risks and opportunities that will affect our business continuity and sustainable growth. Based on the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) established by the Financial Stability Board (FSB), we will disclose our climate change initiatives according to four disclosure items.
Governance
Under the direction of the Sustainability Committee, the Environment Subcommittee plays a central role in considering specific measures and promoting activities related to climate change. The Environmental Subcommittee reports quarterly to the Sustainability Committee on the progress of activities, risk assessment and countermeasures, and receives instructions as appropriate. In addition, with regard to climate change risks, the Sustainability Committee works together with the Risk Management Committee to share information and take other actions.
Climate Change Initiatives:
- ・Climate change scenario analysis
- ・Identification and materiality assessment of short-, medium-, and long-term climate change risks and opportunities
- ・Review of strategic approach to identified significant climate change risks and opportunities
- ・Consideration of specific measures to address climate change risks and opportunities
- ・Promotion of response measures adopted with respect to climate change risks and opportunities
Sustainability Promotion System
Strategy
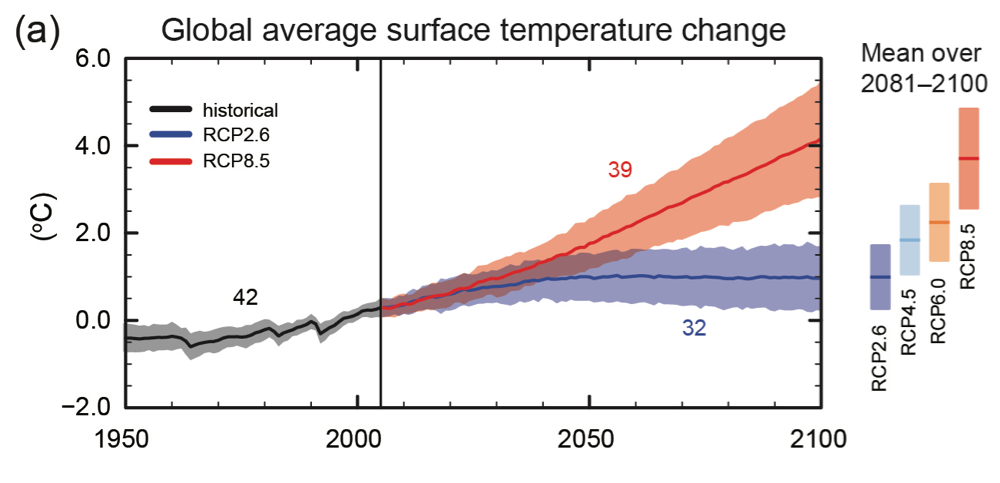
To identify risks and opportunities from climate change, we have set 1.5°C/2°C and 4°C scenarios based on information published by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), the International Energy Agency (IEA), the Japanese government, and other organizations, and analyzed the scenarios for their impact on our business. We have conducted scenario analysis of the impact on our business.
In the 5th IPCC report, climate projections and impact assessments are based on “Representative Concentration Pathways Scenarios,” and analysis is conducted for several scenarios called RCP1.9 to RCP8.5, depending on the difference in radiative forcing at the end of the 21st century. The analysis is being conducted under several scenarios.
Based on these IPCC reports, the International Energy Agency (IEA) and the Japanese government have also studied and published impact scenarios for the energy situation and social aspects under multiple temperature ranges from 1.5°C to 4°C scenarios, and we are conducting scenario analysis based on these scenarios. We conduct scenario analysis by referring to these scenarios.
(Source) IPCC 「AR5 WG1 Summary for Policymakers」
In assessing the risks and opportunities from climate change, we have also established the following evaluation criteria and analyzed the financial impact to identify the effects on our business.
| Evaluation Axis | Overview |
|---|---|
| Temporal Perspective | The extent to which climate change impacts are expected to materialize and affect our business (long term, medium term, short term) |
| Likelihood of Occurrence | How likely is it that the effects of climate change will materialize and affect our business (high, medium, or low) |
| Scope of Impact | The extent to which climate change impacts will materialize and affect our business (large, medium, or small scale) |
<Scenario Analysis>
Assumed period:Through FY2030
Selection Scenarios (1.5℃/2℃):IPCC/RCP2.6, IEA/SDS
(4℃):IPCC/RCP8.5, IEA/STEPS
● Risks
Based on our scenario analysis, under Transition Risk, we identified the possibility that the introduction of a carbon tax or other policy measures to promote climate change action and the response to the market for products that reduce greenhouse gas emissions (products with low carbon emissions during manufacture and use and products that contribute to greater efficiency in healthcare institutions) could have a significant impact on our business performance. We have identified the following risks as potential risks to our performance. In terms of physical risks, we identified the potential for a shutdown of development and manufacturing functions or supply chain disruptions in the event of disaster damage due to extreme weather events to have a significant impact on our operating results.
(High, medium, and low are indicated as H, M, and L, respectively, for the magnitude of the impact on our business performance.)
Transition Risk
| Category | Risk factors | Impact on our company | Countermeasures | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5℃/ 2℃ scenario | 4℃ scenario | |||
| Policy/Regulations | Pricing progression of GHG emissions | M | L | ・Promote energy-saving activities in a systematic manner ・Utilize renewable energy |
| ・The introduction of a carbon tax will increase energy costs for business activities (Sales and Marketing, Development and Manufacturing) | ||||
| Tecnologies | Replacement of existing products and services with low-carbon options | L | L | ・Develop environmentally friendly products (low carbon emissions during manufacturing and use) ・Develop products that contribute to the efficiency of medical institutions (e.g., reduced operation time) |
| ・Expansion of the market for low-carbon related products will result in development and manufacturing verification, which will increase costs (Development and Manufacturing) | ||||
| Markets | Changes in Consumer Behavior | H | L | ・Develop environmentally friendly products (low carbon emissions during manufacturing and use) ・Develop products that contribute to the efficiency of medical institutions (e.g., reduced operation time) ・Proactively address and disclose information in response to climate change-related requests |
| ・Sales and profits will decrease due to inability to respond to market expansion of low-carbon related products (Market) ・Sales and profits will decrease due to inability to respond to climate change-related requests from suppliers (Market) |
||||
| Soaring raw material costs | L | L | ・Develop a collaborative climate change plan with supply chain constituents | |
| ・Raw materials from suppliers, direct costs for energy and freight added to purchase costs, increasing costs (Procurement) | ||||
Physical Risk
| Category | Risk factors | Impact on our company | Countermeasures | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5℃/ 2℃ scenario | 4℃ scenario | |||
| Acute | Increased severity and frequency of extreme weather events such as cyclones and floods | M | H | ・Establish BCP plans for typhoons, floods, and other disasters ・Decentralize development and manufacturing functions ・Promote multiple procurement of raw materials and consider alternatives ・Study alternatives for logistics and early recovery plans ・Promote efficiency in the development and manufacturing verification process |
| ・Sales and profits will decrease due to the suspension of development and manufacturing activities as a result of typhoons, floods, and other disasters (Development and Manufacturing) ・Sales and profits will decrease due to the disruption of logistics functions for product supply caused by typhoons, floods, etc. (Sales and Marketing) |
||||
| Chronic | Changes in rainfall patterns, extremes in weather patterns | L | M | |
| ・Increase costs related to the multilayered procurement of raw materials and energy, and the study of alternatives (Procurement) ・Decrease in the risk of product supply disruptions by considering alternative logistics methods and early recovery plans (Sales and Marketing) ・Increase premium payment costs (Administration) |
||||
● Opportunities
The scenario analysis identified the potential for increased sales through more efficient transportation/manufacturing processes and the development of products that reduce greenhouse gas emissions, which could have a significant impact on our results.
(High, medium, and low are indicated as H, M, and L, respectively, for the magnitude of the impact on our business performance.)
| Category | Opportunity factors | Impact on our company | Countermeasures | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5℃/ 2℃ scenario | 4℃ scenario | |||
| Resource Efficiency | Use of efficient means of transportation/efficient production and distribution processes | M | L | ・Promote efficiency in transportation ・Promote efficiency in manufacturing processes ・Promote recycling of industrial waste |
| ・Efficient delivery methods (e.g., joint delivery) will reduce delivery costs (Sales and Marketing) ・Decrease in manufacturing costs due to consolidation of manufacturing processes (Development and Manufacturing) |
||||
| Use of recycling | L | L | ||
| ・Decrease in raw material costs due to simplified packaging and product design (Development and Manufacturing) ・Decrease in disposal costs through recycling of industrial waste (Development and Manufacturing) |
||||
| Products and Services | Develop and expand low-carbon products/services Changing consumer preferences |
M | L | ・Develop environmentally friendly products (low carbon emissions during manufacturing and use) ・Develop products that contribute to the efficiency of medical institutions (e.g., reduced operation time) ・Proactively address and disclose information in response to climate change-related requests |
| ・Sales and profits will increase due to market expansion of low-carbon related products (Market) ・Sales and profits will increase by responding to requests from suppliers to address climate change (Market) |
||||
| Markets | Access to new markets | L | L | ・Develop medical devices to treat new diseases |
| ・Development of medical devices to treat newly emerging diseases due to climate change will increase sales and profits (Market) | ||||
| Resilience | Participation in renewable energy programs, adoption of energy conservation measures Resource substitution/diversification |
L | M | ・Promote the study of alternatives and multiple lines of raw material procurement ・Study alternatives for logistics and early recovery plans |
| ・Promote the multiline and alternative procurement of raw materials and energy (Procurement) ・Reduce the risk of product supply disruptions by considering alternative logistics methods and early recovery plans (Sales and Marketing) |
||||
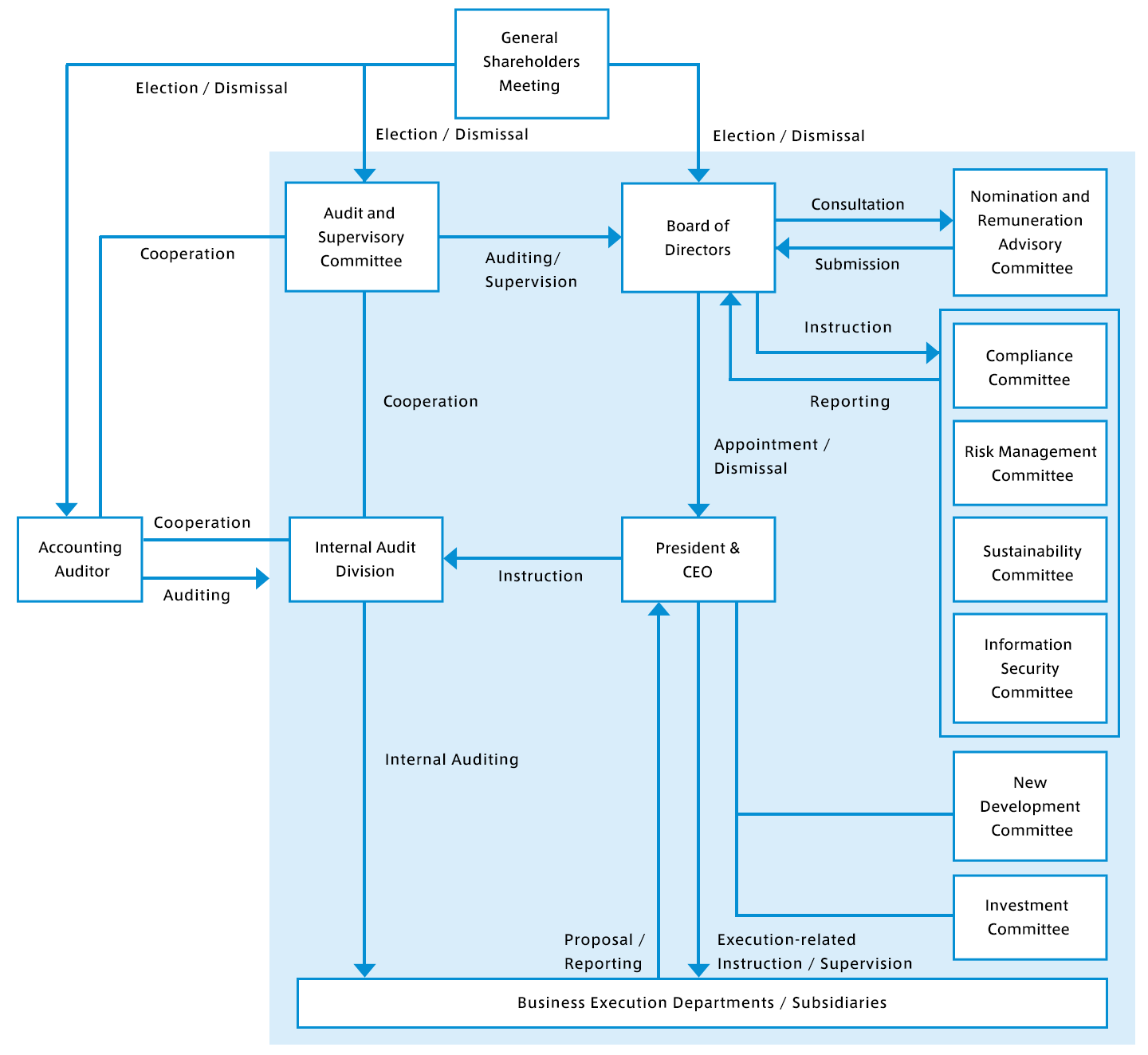
Risk Management
In our company, the Environment Subcommittee play a central role in cross-organizational discussions on climate change-related risks. The Sustainability Committee regularly review the impact level of the risks and the response measures proposed, as well as the progress of the response measures.
Company-wide risk management is carried out by the Risk Management Committee under the Risk Management Regulations. Climate change-related risks are also reported to and discussed by the Risk Management Committee. The Board of Directors receives reports from the Sustainability Committee and the Risk Management Committee on climate change risks for discussion and oversight.
Corporate Governance System
Indicators and Targets
Greenhouse gas (CO2) emissions can be a risk factor regarding our business performance and financial condition due to carbon taxes and other factors. On the other hand, providing products that reduce greenhouse gas emissions can lead to business opportunities. We recognize that reducing CO2 emissions is one of our most important sustainability issues, and we have established indicators for specific initiatives to reduce CO2 emissions and manage our progress.
We have set the following mid- to long-term CO2 emission reduction targets for fiscal 2030, and will promote efforts to reduce CO2 emissions.
| CO2 emissions reduction target |
|---|
| CO2 emissions 50% reduction in 2030 (Against FY3/2021 period ratio) *Targets global Scope 1,2 emissions*1 |
FY3/2023 CO2 emissions (Targets global Scope 1,2 emissions)
(unit: t-CO2)
| Category 1 | Category 2 | Category 3 | Amount of Emissions | Subtotal | Total | (Base Year) FY3/2021 | (Ref.) FY3/2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scope1 | Japan | Sales | 1,425 | 1,453 | 1,454 | 1,488 | 1,436 |
| Manufacturing | 28 | ||||||
| Outside Japan | Sales | 0 | 1 | ||||
| Manufacturing | 1 | ||||||
| Scope2 | Japan | Sales | 612 | 3,208 | 5,158 | 5,462 | 5,284 |
| Manufacturing | 2,596 | ||||||
| Outside Japan | Sales | 8 | 1,950 | ||||
| Manufacturing | 1,942 | ||||||
| Grand Total | 6,712 | 6,950 | 6,720 | ||||
We are currently working to determine Scope 3 emissions*2 and will disclose the result as soon as ready.
*1 Scope 1,2 emissions: Direct and indirect greenhouse gas emissions through the company's operations
*2 Scope 3 emissions: Indirect greenhouse gas emissions from our own supply chain Indirect greenhouse gas emissions from the entire supply chain
Energy-Related Initiatives
Energy Conservation Initiatives
The clean rooms that we use to manufacture medical devices are equipped with power monitoring equipment to keep track of the amount of electricity usage.
In order to maintain the working environment, clean rooms are generally required to operate 24 hours a day, 365 days a year, but at Toda Factory and Oyama Factory, only half of the air conditioning system is used during the night and on holidays to reduce energy use.
We have switched the electricity used at the three factories to new electric power sources, and selected them not only for their cost but also for their lower CO2 emissions.
Utilization of Renewable Energy
We installed solar power generation systems at the Toda Factory in 2017 and the Ichihara Factory in 2021. The total estimated annual power generation of both factories is 286.2 MWh, resulting in a reduction of 126.2 tons of CO2 emissions. We will also promote the use of renewable energy at other factories.

Solar panels at Ichihara Factory
Energy Consumption (Total of R&D and Manufacturing Department)
| FY3/2019 | FY3/2020 | FY3/2021 | FY3/2022 | FY3/2023 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electricity usage(MWh) | 6,176 | 5,806 | 6,211 | 6,268 | 6,193 |
| LPG usage(Kg) | 3,510 | 3,584 | 3,233 | 3,775 | 4,370 |
Effective Use of Water Resources
Since there are many processes in which clean water is used for the production of our products, we are working to reduce the amount of water used at each factory. Specifically, we are working to conserve water resources by installing chillers (cooling water circulation systems) in facilities that require a large amount of tap water for cooling, etc. to recirculate and reuse water once it has been used.
Water Usage (Total of R&D and Manufacturing Department)
| FY3/2019 | FY3/2020 | FY3/2021 | FY3/2022 | FY3/2023 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water usage(㎥) | 16,104 | 14,760 | 12,584 | 16,821 | 13,184 |
Controls for Hazardous Substances
We manage chemical substances in accordance with the laws and regulations of each country to ensure that products do not contain chemical substances that have a negative impact on the environment or the human body.
In addition, the Oyama Factory and Ichihara Factory use EOG (ethylene oxide gas) for product sterilization. Although EOG-based sterilization is highly effective even at low temperatures and is widely used for the sterilization of medical devices, EOG is highly toxic. Therefore, we aim to reduce environmental impact by using a combustion apparatus to decompose the gas containing EOG emitted from the sterilizer, purify it to a harmless level, and release it into the atmosphere.
Waste Management Initiatives
Recycling of Industrial Waste
In addition to our initiatives to reduce and reuse waste, we also focus on recycling in order to contribute to the realization of a recycling-oriented society. We will strive to increase the recycling rate by expanding the scope of waste to be recycled, such as waste generated in the product manufacturing process and products that are no longer usable after their sterilization expiration date.
Recycling Rate of Industrial Waste
| FY3/2021 | FY3/2022 | FY3/2023 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recycling | 90% | 92% | 96% |
Waste Management of Medical Products
Most of the products we handle have expiration dates of sterilization, and we have to dispose of them after the date, except for some that can be re-sterilized. Therefore, it is important for us to manage our inventory to avoid expiration.
For disposal, we ask industrial waste contractors to sort the waste as necessary. In addition, we manage the disposal procedures based on manifests.
Reduction of Cardboard Usage
The logistics centers in Haneda and Osaka use a large amount of cardboard boxes, therefore we reuse them as much as possible and dispose of them after they are stained or damaged.
Between Oyama Factory and Haneda logistics center, reusable transport carts are used for delivery, reducing in the use of cardboard boxes waste.
Recovery of Rare Metal Components Contained in Products
The catheters we handle are tipped with platinum components. We recover the platinum components of the catheters that are defected in the production process and sell them to a precious metal supplier per year for recycling of the rare metals. In addition, as cutting chips are generated in the manufacturing process of the tip electrodes (containing platinum) produced at our contractor, we request them to recover and recycle those chips.
Initiatives in Logistics and Company Vehicles
The products we handle are medical devices and therefore require proper temperature control and storage without exposure to the weather. For this reason, we outsource inventory management and delivery to an external logistics center that has appropriate conditions.
Also, our company vehicles are mostly leased, and hybrid cars are available as option. Hybrid cars account for 95% of all our leased vehicles.

